01 Direct manifestation of "photodamage": damage to children's natural skin barrier
Skin is the largest organ of our human body. It can be divided into epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue from the outside to the inside. The outermost layer of the epidermis is the stratum corneum, which is the skin barrier in a narrow sense. The lowest layer of the epidermis is the basal cell layer, which contains melanocytes. After ultraviolet rays irradiate the skin, the skin will activate its own defense system, and the melanocytes located in the basal layer will produce a large amount of melanin. Melanin absorbs ultraviolet rays to protect skin cells from ultraviolet damage.
Effects of UV rays on skin
The surge in melanin is like a black umbrella held up by the skin, which not only protects the skin from damage, but also causes the skin to darken. When the intensity of ultraviolet rays exceeds the tolerance range of melanin, sunburn will occur, ranging from redness and heat to severe stinging, even redness, swelling, and scarring. These are direct manifestations of "photodamage" . Sunburn, peeling, water scars, etc. are relatively damage to the skin surface, and timely care can be well restored.
Photodamage in neglected children
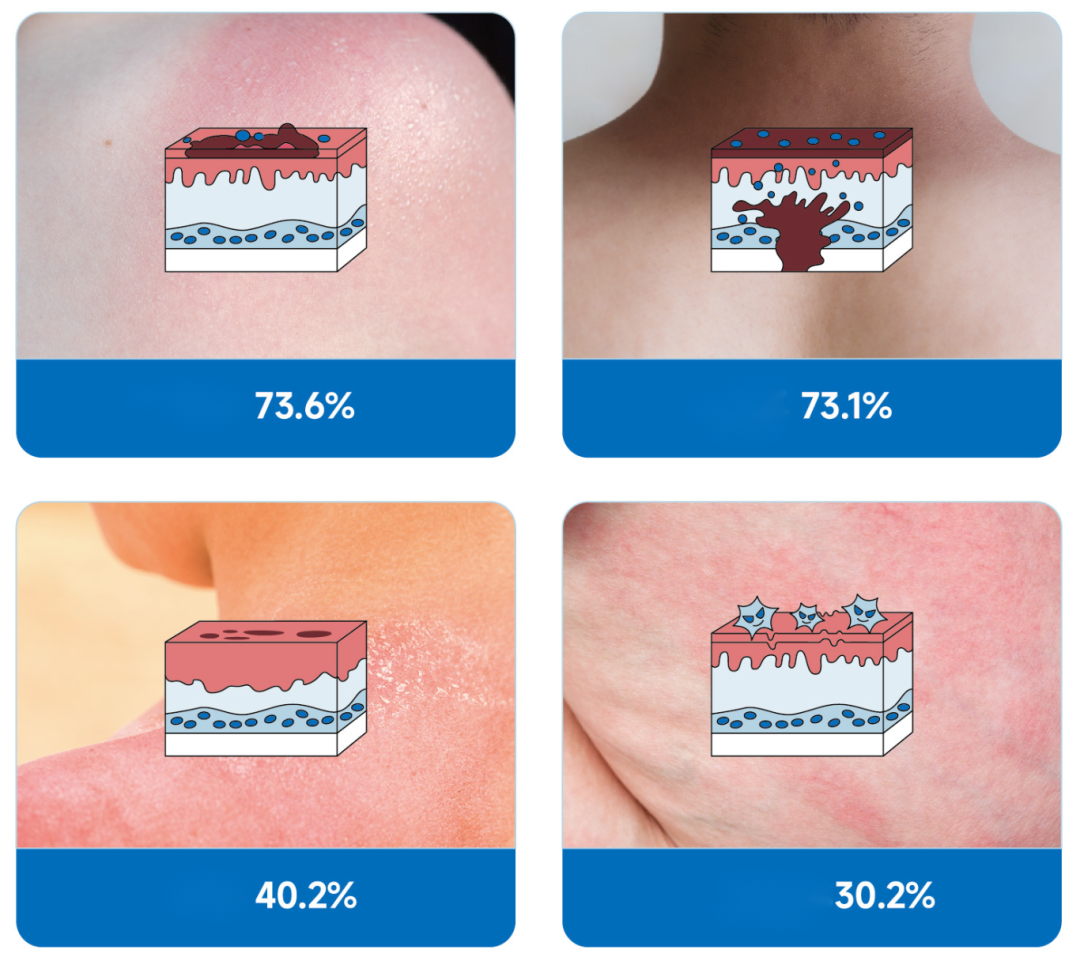
A survey found that 97.2% of children have suffered "photodamage" due to sun exposure.
Among them, sunburn (73.6%), sunburn (73.1%), sunburn (40.2%), and sun sensitivity (30.2%) are the four most important problems. These phenomena all indicate that children's skin barrier is damaged.
02 "Photodamage" may cause cumulative damage
Research has found that "photodamage" may cause cumulative damage:
Sensitive skin
At the 3rd International Allergic Dermatology Exchange Conference, some experts proposed based on adult data that ultraviolet rays can directly or indirectly cause photosensitive skin diseases, such as sensitive skin, acne, etc.
Acne
A study of about 20,000 Chinese college students also came to a similar conclusion. There is a clear correlation between ultraviolet rays and acne. Long-term exposure to lower levels of environmental UVB reduces the risk of moderate and severe acne.
Freckle
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays can also cause pigmentation on the skin, which appears as spots of various shapes. When the initial spots do not penetrate deep into the skin, they can still be reduced or eliminated with proper care.
Melanoma
The American AAD mentions on children’s sun protection that skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States. As long as a person experiences a scarring sunburn in childhood or adolescence, the chance of developing melanoma (skin cancer) in later life will increase. Nearly doubled.
3. How to safely and effectively resist "light loss"?
Physical sunscreen
Such as holding an umbrella, wearing sunglasses, wearing a sun hat, etc.
Use sunscreen
The two most direct indicators of sunscreen effectiveness are SPF value and PA value. It should be noted that the higher the SPF value and PA value, the better. SPF often stands for UVB protection, generally referring to the ability to prevent sunburn. If this value is too high, the protective power will be stronger, but the corresponding sunscreen will be thicker and will easily increase the burden on the skin. Generally speaking, SPF 30 is enough in daily life. The PA value represents the ability to protect against UVA, usually referring to the ability to prevent sunburn. PA+ represents basic UV protection, PA++ represents medium protection, and PA+++ or PA++++ represents high protection.
Reapplying sunscreen is necessary
It should be noted that over time, the sunscreen ingredients will gradually fall off or be decomposed due to sweat, oil secretion or friction, and lose the sunscreen effect. Timely reapplying can effectively extend the protective effect of sunscreen.
Post time: Mar-15-2024

